Tutorial
Tutorial#
We will here consider a problem we have already solved (in the Algebra Tutorial) but use a different interface to do so than Jupyter. The code itself will be the same. The way we run it will differ.
Problem
Rationalise the denominator of \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2} + 1}\)
Open a command line tool:
On Windows search for
Anaconda Prompt(it should be available to you after installing Anaconda). See Starting the notebook server on Windows.On OS X search for
terminal. See Starting the notebook server on MacOS.
Whether or not your are on Windows or MacOS changes the commands you need to type. First, list the directory you are currently in:
$ dir
$ ls
Tip
Throughout this book, when there are commands to be typed in a command line
tool I will prefix them with a $. Do not type the $.
This is similar to using your file explorer to view the contents in a given directory. Similarly to the way you double click on a directory in the file explorer you can navigate to a directory in the command line.
To do this you use the same command on both operating systems:
$ cd <target_directory_name>
$ cd <target_directory_name>
We will do this to navigate to our cfm directoy. For example if, as in the
Algebra Tutorial the cfm directory was on the Desktop
directory we would run the following:
$ cd Desktop
$ cd cfm
$ cd Desktop
$ cd cfm
Attention
The two statements are written under each other to denote that they are run one after the other.
You will now create a new directory:
$ mkdir scripts
$ mkdir scripts
Inside this directory we will run the same command as before to see the contents:
$ dir
$ ls
If you have followed the same steps described in Using notebooks then you will see something similar to:
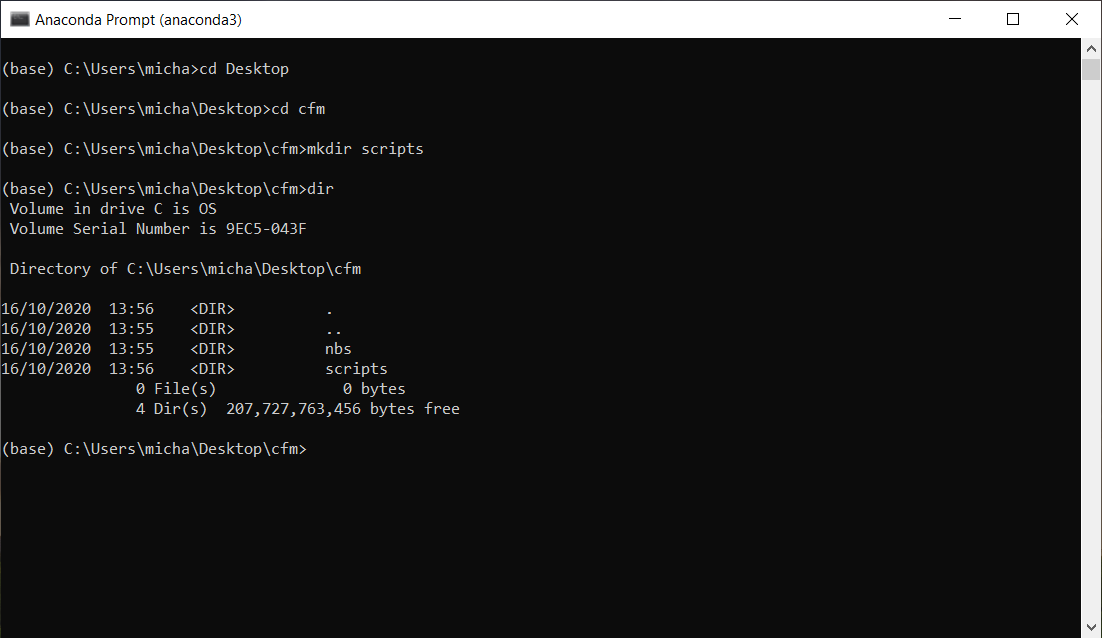
Fig. 12 The contents of our directory on Windows#
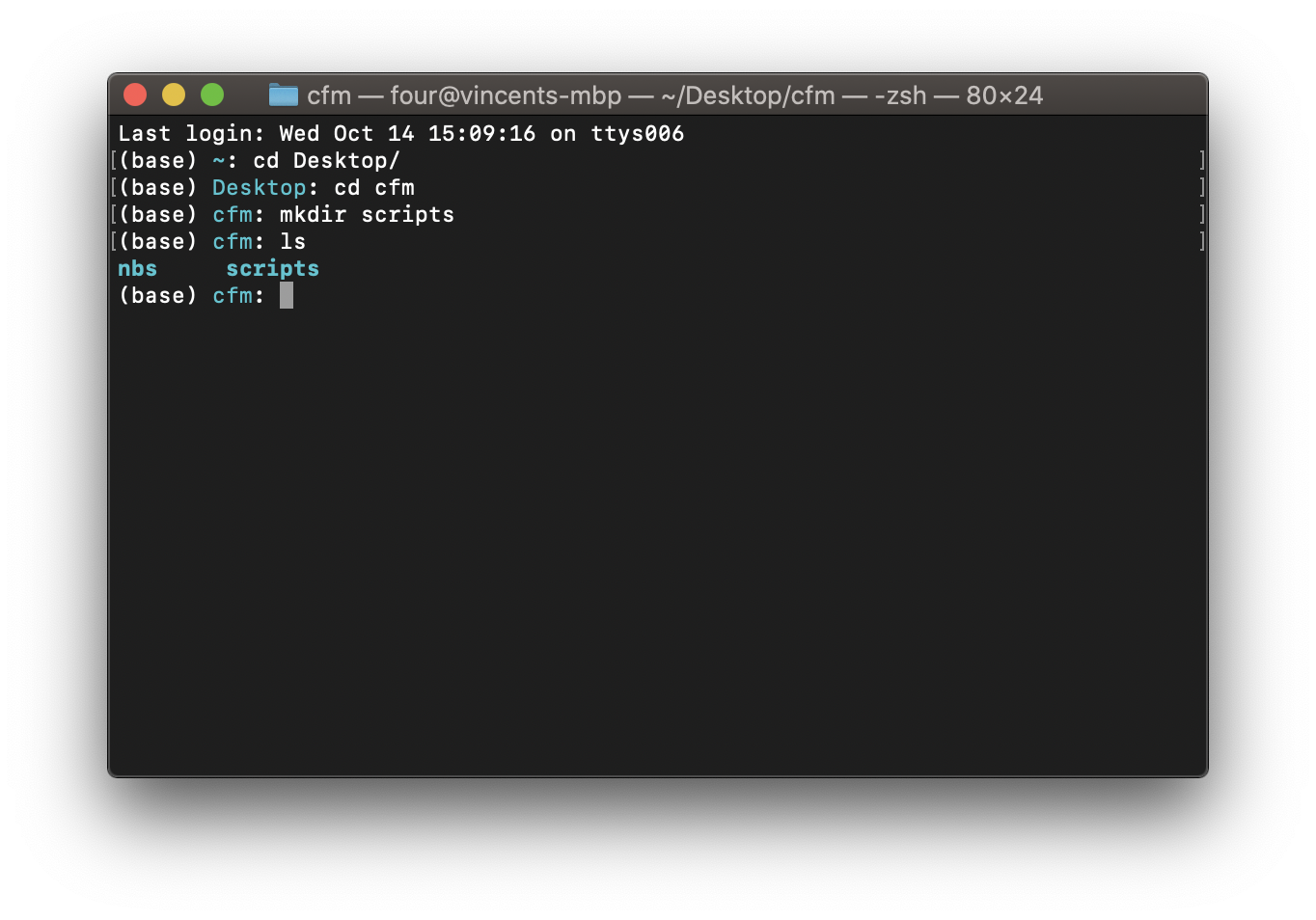
Fig. 13 The contents of our directory on OS X#
Before continuing with this directory you are going to install a powerful code editor.
Navigate to https://code.visualstudio.com.
Download the installer making sure it is the correct one for your operating system (Windows, MacOS or Linux).
Run the installer.
This code editor will offer you a different way to write Python code.
Open VS code and create a new file.
In it write the following (which corresponds to the solution of the problem):
"""
This script displays the solution to the problem considered.
"""
import sympy as sym
print("Question 1:")
expression = 1 / (sym.sqrt(2) + 1)
print(sym.simplify(expression))
This is shown:
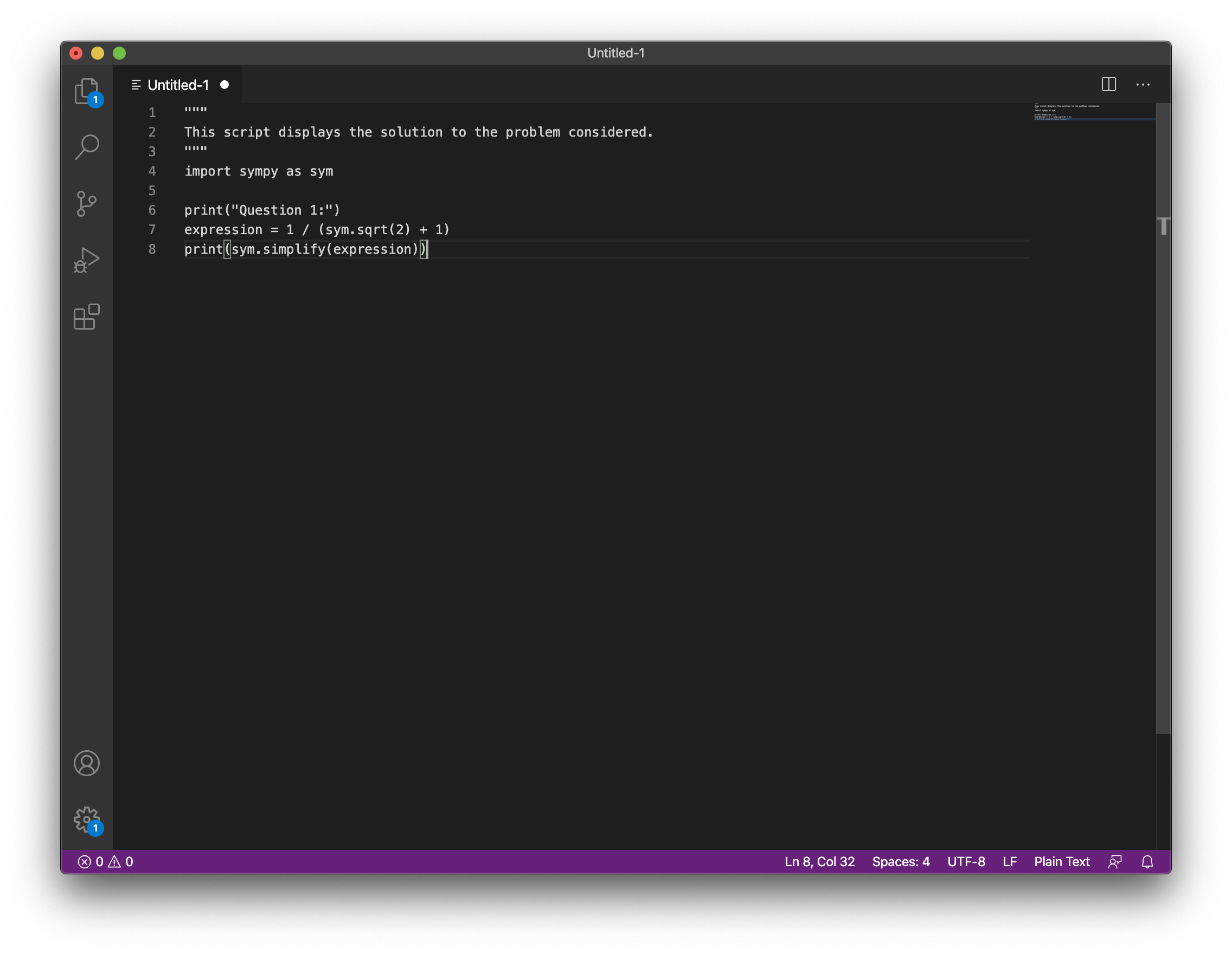
Fig. 14 The code above in VS code#
We will now save this as algebra.py inside the scripts directory we created
earlier.
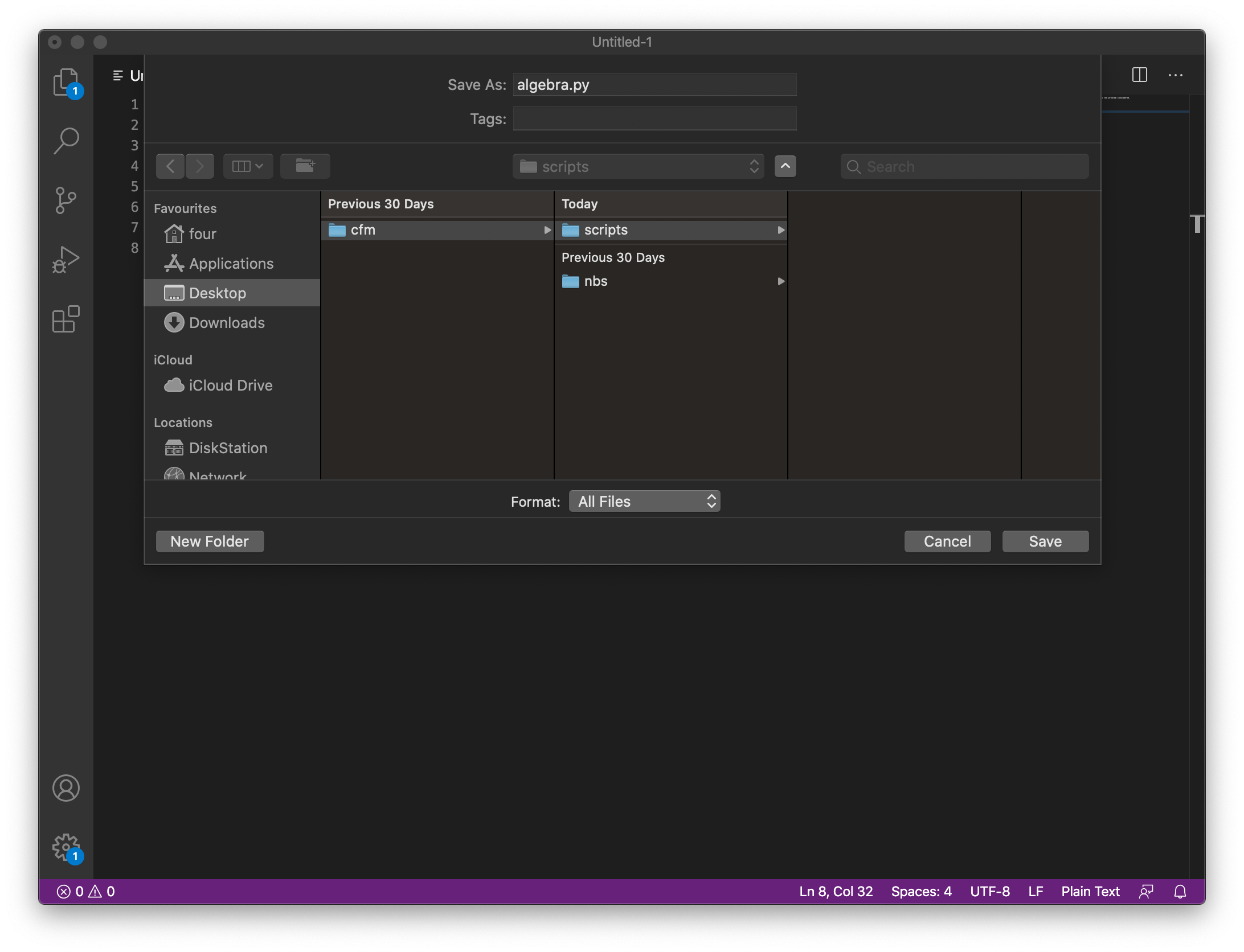
Fig. 15 Saving algebra.py in VS code.#
VScode now recognises the Python language and adds syntax colouring. It also suggests a plugin specific for the Python language. There is more information about plugins in the rest of this chapter.
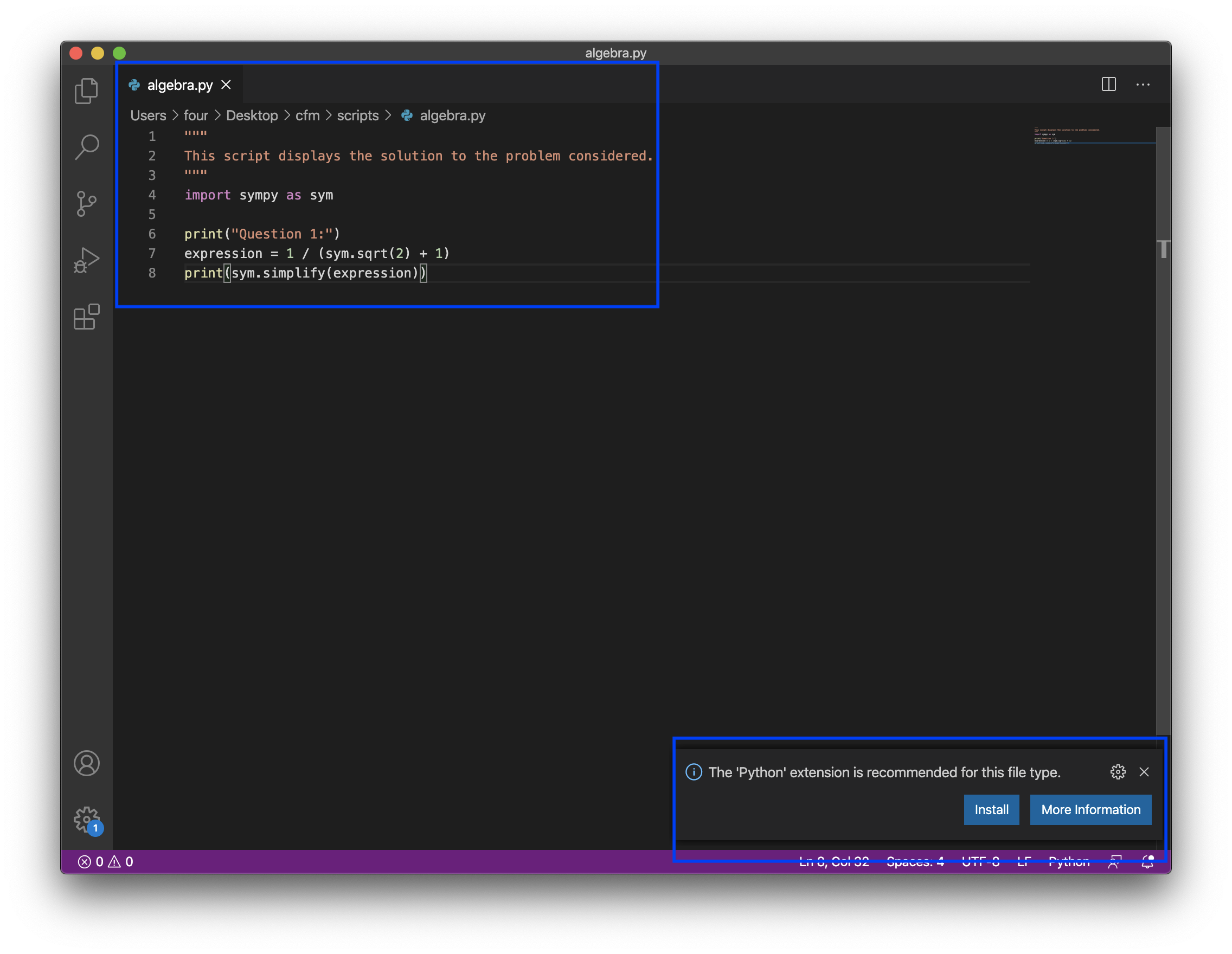
Fig. 16 Syntax colouring and plugin suggestion for the now recognised Python file.#
All you have done so far is write the code. You now need to tell Python to run it. To do this you will use the command line.
Navigate to the scripts directory that you created earlier:
$ cd scripts
$ cd scripts
Now confirm that the algebra.py file is in that directory:
$ dir
$ ls
Now we will run the python code in that script:
$ python algebra.py
When doing that you should see the following output:
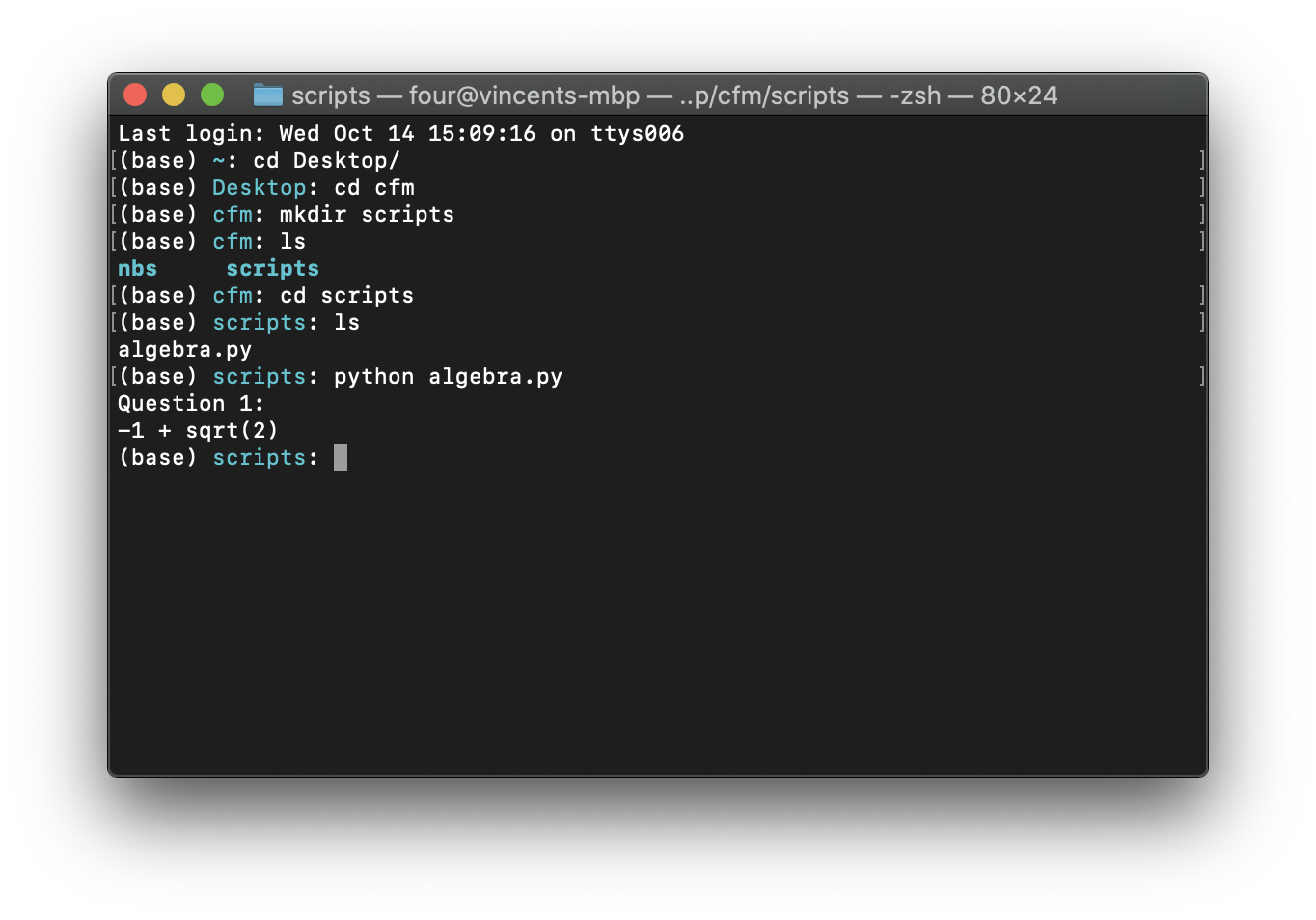
Fig. 17 Output of running the algebra.py script on OS X.#